 Your feet are the mediators between your body and the ground. So they must be sturdy enough to support the body’s weight while being flexible enough to conform to varied terrain. Foot design meets both of these requirements perfectly by consisting of 36 bones for flexibility, bound tightly together by a web of ligaments for strength. Your feet literally take a pounding everyday, with the average person taking more than 10,000 steps daily. During running or going down stairs, up to 3 times the body’s weight can come bearing down on the feet. The healthy, long term foot function requires, therefore, that the load bearing function of the skeletal system as well as the shock absorption function of the muscular system function properly throughout the entire leg. (more…)
Your feet are the mediators between your body and the ground. So they must be sturdy enough to support the body’s weight while being flexible enough to conform to varied terrain. Foot design meets both of these requirements perfectly by consisting of 36 bones for flexibility, bound tightly together by a web of ligaments for strength. Your feet literally take a pounding everyday, with the average person taking more than 10,000 steps daily. During running or going down stairs, up to 3 times the body’s weight can come bearing down on the feet. The healthy, long term foot function requires, therefore, that the load bearing function of the skeletal system as well as the shock absorption function of the muscular system function properly throughout the entire leg. (more…)
Your Hips are the Foundation to your entire Body Motion Machine.
 Your pelvis is located at the center of your musculo-skeletal system. It is the largest bone of your body and surrounded by the strongest muscles groups. It therefore serves as the base of support for practically all body movement – up-down, forward-backward and side-to-side.
Your pelvis is located at the center of your musculo-skeletal system. It is the largest bone of your body and surrounded by the strongest muscles groups. It therefore serves as the base of support for practically all body movement – up-down, forward-backward and side-to-side.
This is why it is crucial that the pelvis is properly positioned within your body and within the line of gravity.
“Everything Hurts! Syndrome” / Dr. Skokan Martin/
Extended periods of sitting or standing mixed with one-sided activity such as can be found at most worksites in the office, in the medical practice, in the car, etc. quickly cause the large muscle groups around the pelvis to stop functioning symmetrically. As a result the pelvis is no longer maintained level from left to right as seen from the front and no longer properly angled from front to back when viewed from the side. The pelvis becomes twisted out of alignment resulting in a chain reaction of instability going out in all directions.
Upward, the vertebrae, shoulders, elbows, wrists and fingers are all forced to function out of alignment. (more…)
The Rotator Cuff
The Rotator Cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that connecting the humerus (upper arm) to the scapula (the shoulder blade). The four muscles of the rotator cuff are:
- Musculus Supraspinatus – The supraspinatus abducts, or elevates, the shoulder joint.

- Musculus Infraspinatus – The infraspinatus externally rotates the shoulder joint.
- Musculus Subscapularis – The subscapularis muscle works to depress the head of the humerus allowing it to move freely in the glenohumeral joint during elevation of the arm
- Musculus Teres minor – The teres minor muscle externally rotates the shoulder joint.
The four muscles also stabilize the head of the humerus in the glenohumeral joint, or shoulder joint. The muscles, tendons and other tissues form a cuff around the humerus. The Rotator Cuff tendons provide stability to the shoulder, the muscles allow the shoulder to rotate. (more…)
The Knee – is the largest joint in the body
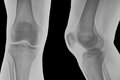 The knee is te biggest and the most complex joint in the human body. The knee is the most likely to be injured, than is any other joint in the body.
The knee is te biggest and the most complex joint in the human body. The knee is the most likely to be injured, than is any other joint in the body.
The knee is made up of 4 bones and an extensive network of ligaments and muscles.
The four main bones:
- Femur (thigh bone) – the longest and the largest bone in the body, part of the hip joint and part of the knee joint
- Tibia (shinbone, shankbone) – is the larger and stronger of the two bones int the leg below the knee, and connects the knee with the ankle bones.
- Fibula (calf bone) – is placed on lateral side of the tibia, with which it is connected above and below, and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint
- Patella (knee cap, kneepan) – is a thick bone, which articulates with the femur and covers and protects the anterior surface of the knee joint. (more…)
Bursitis – signs and symptoms
 Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa.
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa.
Bursae – are fluid-filled sacs that cushion areas of friction between tendon and bone or skin. The major bursae are located adjacent to the tendons near the large joints, such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees and heels. Humans have bursae throughout the body. When the condition called bursitis occurs, the normally slippery bursa becomes swollen and inflamed.
Two types of bursits:
- Acute disease: – when the affected joint takes on a reddish color, it is painful and is usually caused by infection.
- Chronic disease: it may be the result of having suffered an acute bursitis in advance, or another cause is that the patient has had joints injuries on several occasions. (more…)
Myositis
Myositis is a general term for inflamation of the muscles. Myositis can take several forms, usually develops slowly over time and can range in severity from mild to debilitating. Myositis may be associated with inflammation in other organs, including the joints, heart, lungs, intestines and skin. Both children and adults can get it.
- trauma
- infection
- strain
- autoimmune disease – it is not known what triggers the immune system’s attack –
Metabolic syndrome
 Metabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Metabolic syndrome is also known as cardiometabolic syndrome, insulin resistance syndrome.
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Metabolic syndrome is also known as cardiometabolic syndrome, insulin resistance syndrome.
Metabolic risk factors are:
- Abdominal obesity or “having an apple shape”- Visceral fat in the abdominal area is a greater risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
- A high triglyceride level (Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood)
- A low HDL („good”) cholesterol level.- This is because it helps remove cholesterol from your arteries. A low HDL cholesterol level raises your risk for heart disease.
- High blood pressure – Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood. If this pressure rises and stays high over time, it can damage your heart and lead to plaque buildup.
- High fasting blood sugar – Mildly high blood sugar may be an early sign of diabetes. (more…)
Signs and sympomtoms of arthritis
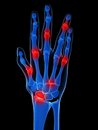 Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints, which results in pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. There are over 100 different types of arthritis.
Arthritis is inflammation of one or more joints, which results in pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited movement. There are over 100 different types of arthritis.
The signs and symptoms of most forms of arthritis are quite similar. Many of the following symptoms common in arthritis are also common in other conditions unrelated to arthritis. However, a good policy to follow is to seek medical evaluation of any symptom, or combination of symptoms, that does not go away within a few days or, at most, a few weaks. A painfull, red and swollen joint calls for immediate medical attention.
General signs and symptoms are:
- Pain and swelling in your joints
- Redness or heat in any of the joints
- Generalized aching and stiffnes of the joints
- Creaky bones
- Loss of motion of the affected joints
- Loss of strength
- Fatique
- Deformity of the joints (over time) (more…)
Isometric exercise – physical therapy
 Isometric exercises are a type of srength traininging in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction.
Isometric exercises are a type of srength traininging in which the joint angle and muscle length do not change during contraction.
Isometric exercise, are a great way to buid strength, power, rehabilitation, and a nice body.
Physical therapists often use isometric exercises with individuals who are recovering from an injury or who have experienced joint inflammation due to arthritis or another joint condition. Isometric exercise are done as a push or pull and can be done with bodyweight, free weights or weight machines or pushing against a wall or other object.
Isometric training is primarily reserved for initial strength training during physical therapy.
Joint Pain
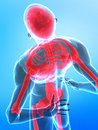 Joint pain, occurs when muscles move the bones in ways that violate the body’s design. It is a form of high-priority communication alerting us of danger and encouraging remedial action. Ignoring or dampening pain signals will only allow joint damage to worsen as the fundamental causes are left untreated.
Joint pain, occurs when muscles move the bones in ways that violate the body’s design. It is a form of high-priority communication alerting us of danger and encouraging remedial action. Ignoring or dampening pain signals will only allow joint damage to worsen as the fundamental causes are left untreated.
Painful lower backs, shoulders, necks, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, feet and so on are all a result of compromised postural alignment leading to excessive wear within the moving, load-bearing parts of the system. Everytime we turn around, take a step, move our wrist, etc. the deviated joint experiences another micro trauma. Life literally becomes a daily grind as the joint wears down and becomes debilitatingly painful. (more…)
